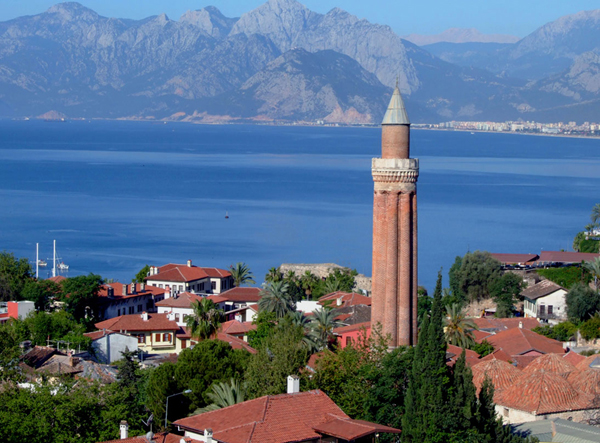
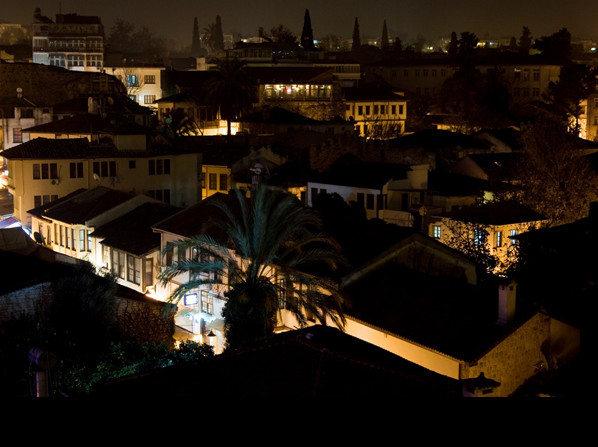
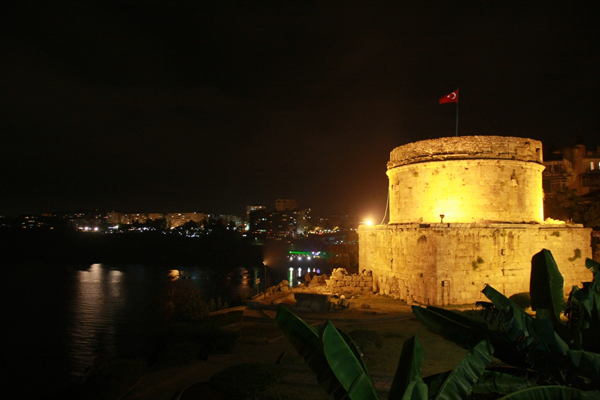
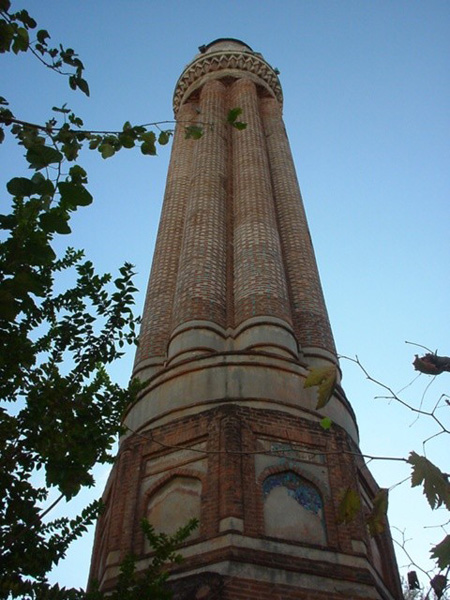
Antalya is only a few thousand years "young" and yet has witnessed the nine thousand year old Anatolian history and the birth of the eldest civilizations of the world. Discover Antalya at the Mediterranean Coast with a huge historical and cultural treasure. Start your journey into the past in Belek and Antalya, while the sun sparkling on the sea accompanies you on every step you take...
-
DISCOVERING BELEK

-
ANTALYA -A MEDITERRANEANDREAM

-
THE MUSEUM OF ANTALYA

-
KALEİÇİ -THE ANTIQUECITY CENTER

-
THE HADRIAN’S GATE

-
THE TOWER OF HIDIRLIK

-
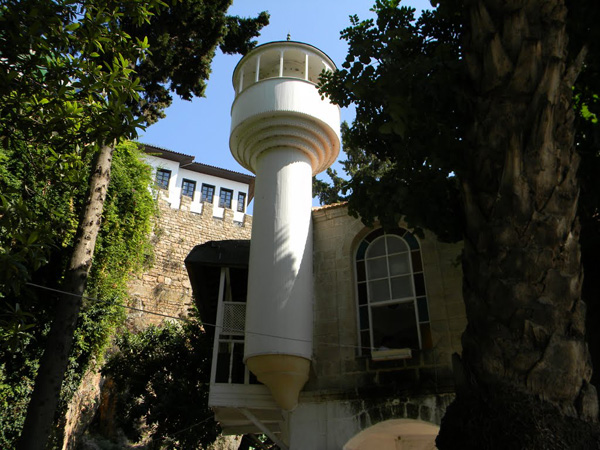
THE KESİK MİNARE MOSQUE

-
THE BUILDINGS AROUND THE YİVLİ MİNARET

-
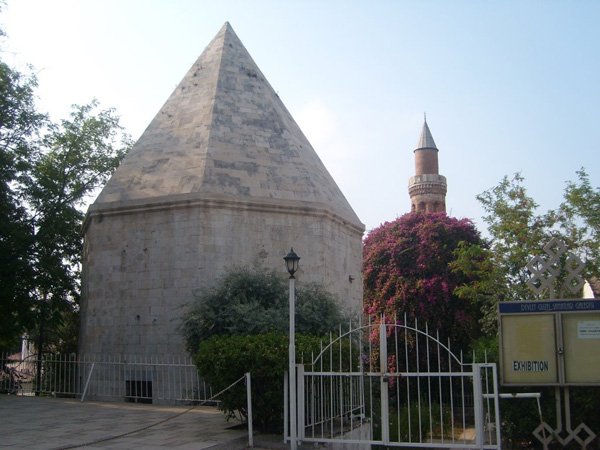
ZİNCİRKIRAN TOMB

-
NİGAR HATUN TOMB

-
İSKELE MOSQUE

-
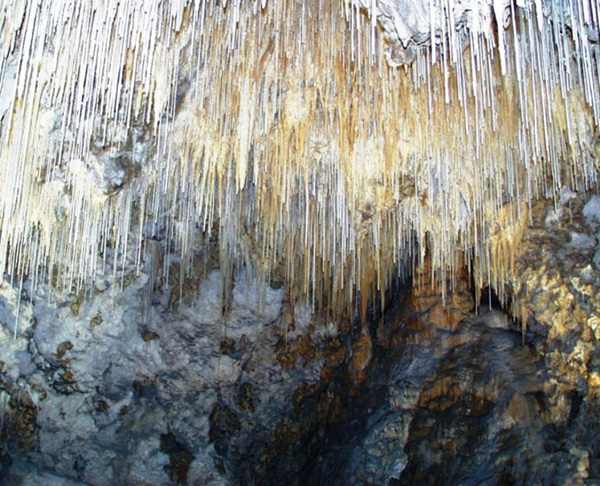
DAMLATAŞ CAVE

-
ZEYTİNTAŞI CAVE

-
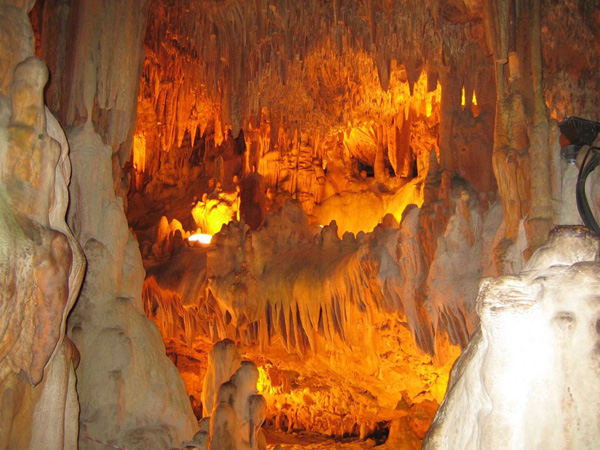
DİM CAVE

-
ASPENDOS

-
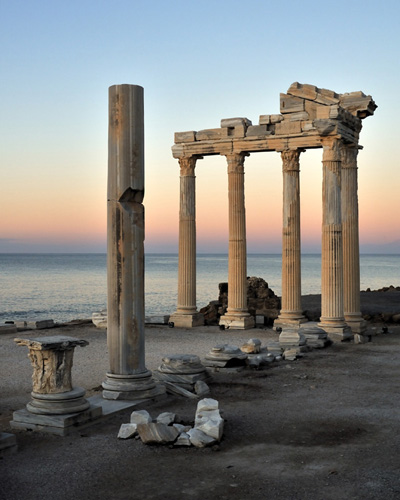
SIDE

-
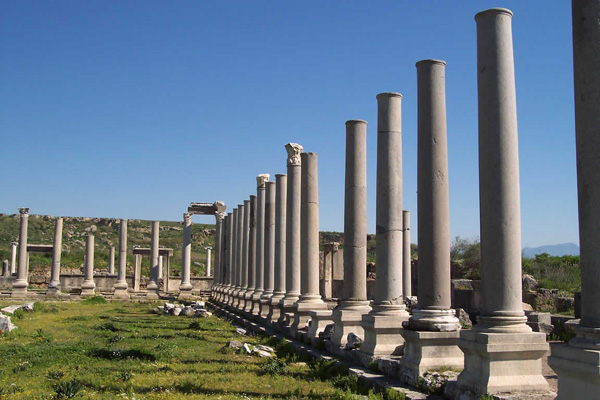
PERGE

-
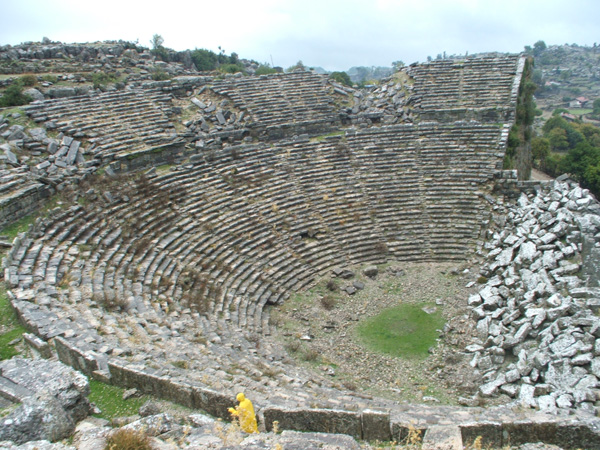
SILLYON THE ANTIQUE CITY

-
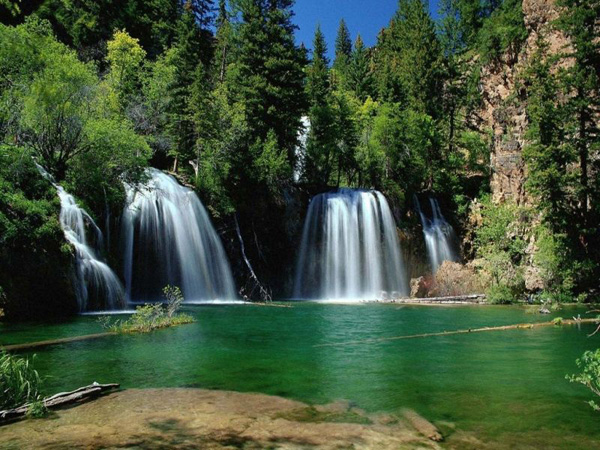
KURŞUNLU WATERFALLS

-
DÜDEN WATERFALL

-
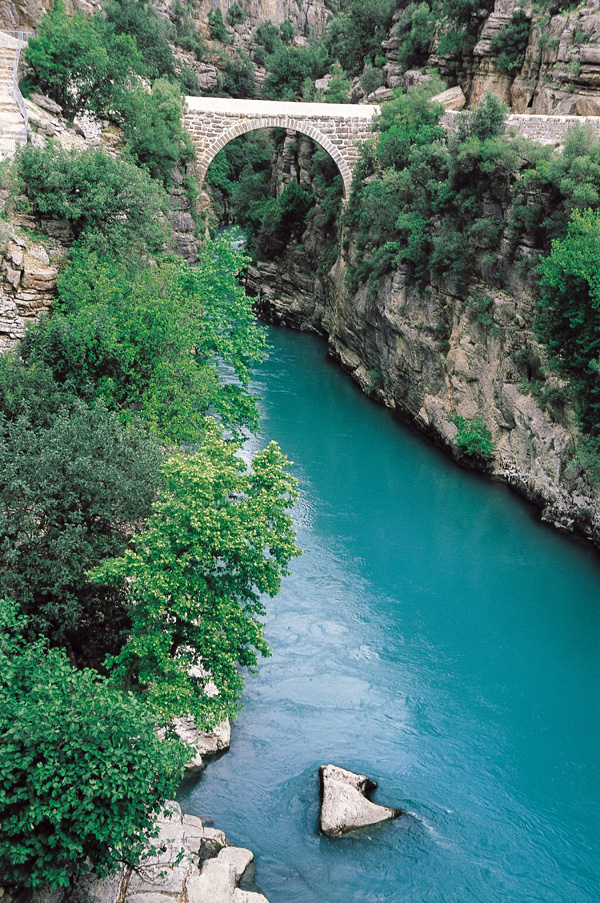
KÖPRÜLÜ KANYON NATIONAL PARK

-
SELGE